
Prostatitis is one of the most common urological diseases in men.
According to WHO research, at least 30% of men aged 20 to 50 suffer from this disease, and each year this insidious disease affects more and more young people. Inflammation of this organ has been reported even in children aged 15 to 16 years.
The causes of chronic prostatitis
The disease itself is acute and chronic. Chronic prostatitis develops with premature or ineffective treatment of acute prostatitis. Unfortunately, in the chronic form of prostatitis, a person cannot count on a complete recovery.
Due to the development of the disease, congestive (congestive) and infectious prostatitis are also distinguished.
Congestive prostatitis occurs with circulatory disorders in the pelvic region, as well as stagnation of prostate secretions. The low permeability and the regular accumulation of blood in this area over time lead to the development of foci of inflammation. As a result, the prostate becomes deformed, which in turn has a negative effect on neighboring organs.
An enlarged organ can contract the urinary tract, disrupting a person's urinary function, and also pressure the bladder, causing a frequent urge to urinate. The development of prostate congestion is most often influenced by a sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits and obesity also increase the likelihood of illness.
The cause of infectious diseases is much more difficult to discover than congestive diseases, because the disease can develop based on many venereal and fungal diseases. An infection, which enters a person through sexual contact, spreads throughout the body, but the first to appear is the prostate, where most pathogens accumulate. The multiplication of the bacteria in this organ over time leads to its inflammation and, later, to the development of a kind of purulent foci (even after healing, scars remain).
The infection does not stop in the prostate, some bacteria pass through the urinary channels, entering the bladder and kidneys, which leads to regular urination.
However, infectious prostatitis is not always the result of sexually transmitted diseases. There are thousands of bacteria and microorganisms in the human body that regularly come from the world around us. Immunity deals easily with most of them, unless, of course, it is weakened by the negative effects of smoking, alcohol, constant stress and neurosis. In these cases, the immune system is not able to fully regulate the development of bacteria or fungi, causing their uncontrolled multiplication to occur, eventually affecting the prostate.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
The first signs of chronic prostatitis appear for the first time in the regular need to urinate and discomfort in the perineum, similar to pain. This can be felt mainly if you lightly press the lower abdomen or the anus.
The irregular flow of urine is considered another symptom of chronic prostatitis. Spraying in different directions indicates deformation of the muscle, which must block the urinary canal (the muscle is located at the base of the prostate).
The weakness of the jet is also negative signs, which indicates more about the infectious character of the development of the disease, in which several organs of the genitourinary system are affected at the same time. In some cases, there are problems with erection, but more often they arise from a person's difficult psychological state.
Diagnosis of diseases
The diagnosis in the early stages of prostatitis is the same, whether normal or chronic, infectious or stagnant. Treatment is most often performed by andrologists (in some cases, urologists).
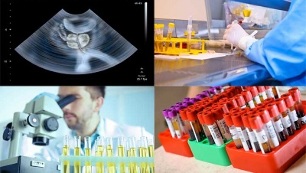
After consultation and internal examination, the doctor will write a recommendation for testing:
- Smear.The collection is performed by means of a special probe, which is inserted into the patient's urethra (the analysis allows to find out which bacteria and how much are in the patient's urinary canal). Before taking the test, you should avoid urinating for about 4 hours.
- Analysis of prostate juice.The prostate has a porous structure and, with inflammation, some parts of that organ are simply blocked. Although the inflammatory process is in full swing in them, regular examinations show nothing. This is where the secret analysis (prostate juice) comes to the rescue. The doctor massages the prostate through the anus, thereby squeezing the secretion from the inflamed areas and then collecting it from the urethra.
- Urinalysis.Usually given after a smear, it allows you to discover the pathology of the bladder and kidneys.
- Blood test- An analysis is performed for infections.
- Ultrasound- examination of the prostate, bladder and kidneys.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis in men
After completing all analyzes, the andrologist proceeds with treatment. In the case of congestive prostatitis, treatment is simpler. As a rule, it consists of taking antibiotics and immunosuppressants. The inflammation is removed with suppositories, which must be inserted into the anus.
In infectious prostatitis everything is much more complicated, for a more accurate diagnosis, some tests will have to be redone again. Treatment will be prescribed depending on the severity of the infection. Most of the time, they are droppers and antibiotics. The second step will be immunocorrection and elimination of toxins from the body. Along with drug treatment, prostatic massages and physiotherapy (electrophoresis and magnetotherapy) are used.
The insidious character of infectious prostatitis lies in the fact that, with a supposedly complete cure, some of the pathogens still remain in the body and multiply over time, triggering inflammation of the prostate again. To avoid this, it is recommended to retake the tests regularly and be examined by a doctor.
Often, even after complete recovery, the patient complains of discomfort in the perineal region and frequent urge to urinate. This situation is not uncommon. The fact is that even after the removal of the inflammatory process, scars remain on the organ, which interfere with its normal functioning. To eliminate this problem, there are several drugs (suppositories with enzymes) that aim at the resorption of scars.
Prevention of chronic prostatitis
The treatment of chronic prostatitis aims to maximize the prolongation of remission and the timely suppression of new inflammatory processes. To achieve long-term remission and thus avoid regular visits to the hospital, you need to radically change your lifestyle.
To start with, don't catch a cold under any circumstances. Any drop in temperature, even the slightest, can cause an exacerbation. It is enough to ride the bus in a cold seat or sit in a draft. If possible, avoid sedentary work or do a five-minute warm-up at least once an hour, say goodbye completely to all bad habits:Smoking and drinking alcohol are strictly prohibited!
In addition, it is important to follow a special diet for chronic prostatitis. It is not recommended to eat smoked products, excessively greasy foods, heavily carbonated drinks and some types of spices (spicy condiments).

Include in your diet:
- chicken;
- fish;
- fermented dairy products (cottage cheese, kefir, low-fat milk cream);
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- dear.
The use of pumpkin seeds has a very positive effect on the prostate.
If you have been diagnosed with chronic prostatitis, don't be depressed! Yes, the disease is quite complex, but if you follow all the doctor's recommendations and lead a healthy life, the pain and constant discomfort will no longer bother you for a long time. Careful care for your health and regular checkups by an andrologist will allow you to live a full and colorful life!
























